This procedure can be both diagnostic and operative, making it a valuable tool in the diagnosis and treatment of various uterine conditions.
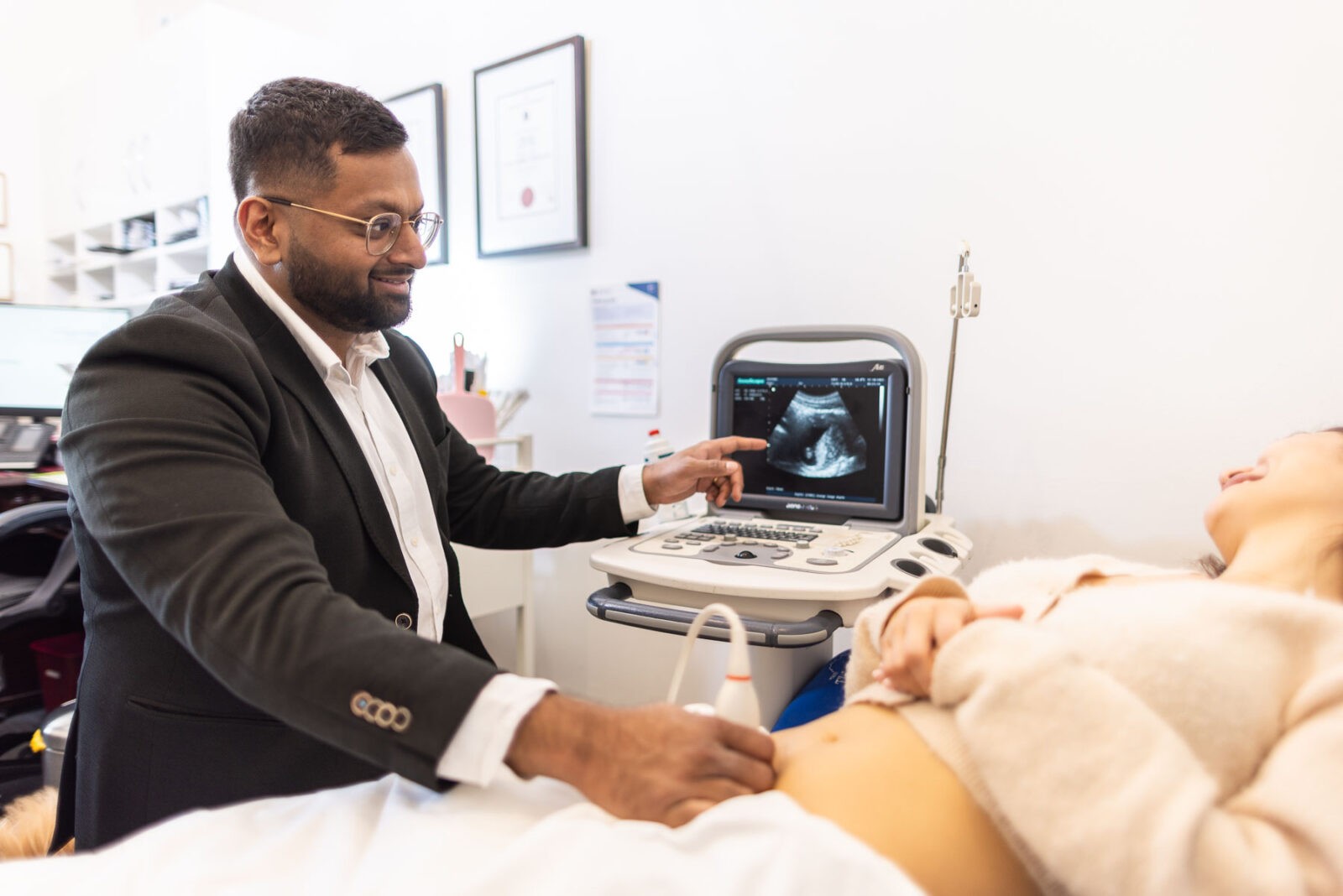
Hysteroscopic surgery involves the use of a hysteroscope – a thin, lighted tube inserted through the vagina and cervix into the uterus.
This tool allows the surgeon to view the uterine cavity on a screen and perform various procedures without external incisions.
This technique is highly effective for diagnosing and treating numerous uterine conditions with minimal invasiveness.
Endometrial hyperplasia is a condition characterised by the thickening of the uterine lining (endometrium), often caused by excess oestrogen without sufficient progesterone.
While hysteroscopy is generally safe, potential risks and complications include:
At MIGYNAE, we understand the unique health needs of women and are dedicated to providing personalised, high-quality care.
Our team of experienced gynaecologists utilises the latest technologies, including hysteroscopic surgery, to ensure the best outcomes for our patients.
To learn more about hysteroscopic surgery or to schedule a consultation, please contact us.








We are a general gynaecology and infertility treatment clinic based in Melbourne, dedicated to the latest minimally invasive gynaecological diagnostic and surgical techniques. We are leaders in laparoscopic and cutting-edge robotic surgery.
If you have a question about a condition or treatment, or would like to book an appointment, please get in touch.